Fast Look
The Fed raised rates of interest by 50 foundation factors this week.Economists count on a smaller 25-basis-point hike on Feb. 1, 2023.Rates of interest on bank cards and mortgages will proceed to extend because of this.Financial savings account yields may enhance as nicely.The Fed hopes to cease mountain climbing charges in Q1 or Q2 2023, however that is dependent upon inflation and the financial system.
The Federal Open Market Committee of the Federal Reserve hiked the carefully watched federal funds charge by 50 foundation factors at its assembly this week. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell introduced the transfer at 2pm Jap Time on Wednesday, Dec. 14.
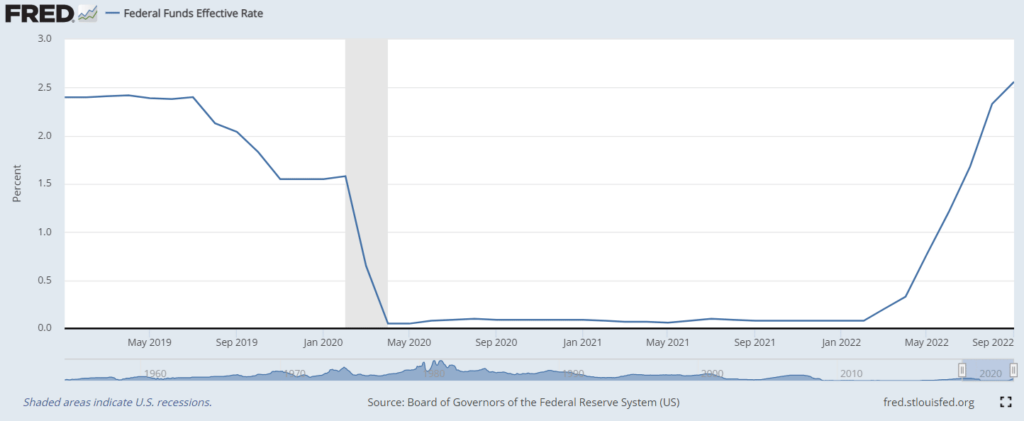
The FOMC’s December charge enhance is the newest in a collection of hikes starting early this 12 months. It would enhance the goal federal funds charge to a spread of 4.25% to 4.50%, a 50-basis-point leap from the November vary and a 425-basis-point enhance from the start of 2022. The upper charge instantly elevated borrowing prices for customers and companies.
Discover out what to anticipate from the Fed’s subsequent assembly, what it means for the broader financial system, and how one can put together your funds for what’s to return.
The FOMC’s December 2022 Assembly
The market’s expectation for a 50-point hike got here amid commentary by key Federal Reserve governors, together with Christopher Waller and Chair Powell himself, that the FOMC may average its aggressive stance.
The Fed raised charges at an unprecedented tempo in 2022 amid persistently excessive inflation, and up to date financial knowledge counsel their efforts have paid off. The labor market is moderating, the red-hot housing market is cooling, and most significantly, inflation seems to be peaking.
Not like in November, when just about everybody anticipated a 75-point enhance, there was some uncertainty across the measurement of the December hike. The Fed may have (however didn’t) shock the market with one other 75-point hike. Much less seemingly however nonetheless potential was a 25-point increase. Really, the consensus view of a 50-point hike panned out.
The market would have taken a 75-point enhance as an indication that the Fed believes inflation isn’t but underneath management. Shares and bonds would seemingly have bought off exhausting on this state of affairs.
A 25-point enhance would have despatched the alternative sign about inflation, however may additionally increase considerations that the Fed thinks the financial system is in worse form than it seems. It’s not clear how the market would have reacted to a smaller-than-expected hike.
As is customary, merchants held their positions till Chair Powell’s customary post-announcement press convention, when he answered questions from monetary journalists determined for perception into the FOMC’s considering. If previous is prologue, his solutions may precipitate a brand new spherical of market volatility. (Or not.)
We weren’t in attendance, however we’d ask him these 4 questions if we may.
Why Is the FOMC Elevating Curiosity Charges Once more?
In a phrase, inflation.
Regardless of indicators of a peak, annualized inflation stays above 8%, far larger than the Federal Reserve’s 2% goal. The FOMC seems to be rerunning the Fed’s playbook from the early Eighties, when then-Chair Paul Volcker pushed the fed funds charge to 19% in a bid to quash sky-high inflation.
How Do Fed Funds Fee Hikes Have an effect on the Financial system?
The federal funds charge is a key benchmark rate of interest for banks and different lenders. Elevating it will increase the price of the short-term loans most monetary establishments have to function usually. They cross these prices to their debtors by way of larger rates of interest on bank cards, actual property loans, and enterprise loans and credit score strains.
The correlation isn’t all the time good, however financial exercise tends to sluggish as borrowing prices enhance. Customers purchase much less on credit score and postpone main purchases. Companies delay or cancel deliberate investments. They could lay off contractors and workers if they will’t management prices elsewhere.
With companies making much less cash and fewer folks drawing paychecks, a suggestions loop develops. Demand for items and companies falls. The financial system slows additional, perhaps tipping into recession. Declining demand helps cool inflation, however on the (hopefully non permanent) price of livelihoods and earnings.
When Will the Fed Cease Elevating Charges?
Economists count on the federal funds charge to high out within the first or second quarter of 2023. They count on a terminal charge — the very best the Fed will let the funds charge get earlier than it takes motion — of between 4.75% and 5.25%, in response to the FedWatch predictive software. However some banks count on a terminal charge nearer to six%, which might trigger much more financial ache.
As soon as it hits the terminal charge, the Fed will most likely preserve charges regular for some time, until the financial system is in actually tough form. Then it’ll pivot — market-speak for starting a rate-reduction cycle. Markets like it when the Fed pivots as a result of it means decrease borrowing prices and, often, larger enterprise earnings.
Will the Fed Trigger a Recession?
In accordance with Reuters’ October 2022 economist survey, it’s likelier than not. About 65% of respondents predicted a U.S. recession by the fourth quarter of 2023.
Chair Powell appears unbothered by the potential for a recession. Although he hasn’t stated outright that he’s rooting for a recession, he’s on the file saying that asset costs (particularly actual property values) want to return down. And in August, he advised attendees on the carefully watched Jackson Gap Financial Symposium that the Fed’s dedication to combating inflation was “unconditional.”
The inventory market tanked as he spoke.
What the December Fee Hike Means for Your Funds
What does the Federal Reserve’s newest rate of interest hike imply in your pockets? 4 issues:
Your Credit score Card Curiosity Fee Will Go Up. Like clockwork, bank card corporations increase rates of interest in lockstep with the Fed. Anticipate your bank card charges to extend by 50 foundation factors inside every week of the speed hike.Your Financial savings Account Yield May Enhance. The connection between financial savings yields and the federal funds charge isn’t fairly as robust, but it surely’s nonetheless there. Banks simply have a tendency to lift yields extra slowly than the Federal Reserve as a result of they make cash off the unfold between what they pay clients and what they themselves pay to borrow. Your Fastened Mortgage Fee Received’t Enhance. Your fastened mortgage charge is, nicely, fastened. At this level, refinancing most likely isn’t in your greatest curiosity, so simply sit again and benefit from the charge you locked in when cash was cheaper. When you have an adjustable-rate mortgage, your charges will go up, and it could be time to contemplate refinancing earlier than it will get worse.Your Retirement Portfolio Will Stay Unstable. It has been a tough 12 months for shares and bonds. We’re not within the enterprise of stock-picking, but it surely’s a good guess that market volatility will persist as a consequence of ongoing financial uncertainty and uncertainty round simply how far the Fed will go to battle inflation.
Your Private Finance Playbook: What to Do As Curiosity Charges Rise
The negatives of upper rates of interest outweigh the positives, but it surely’s not all dangerous. Do this stuff now to guard your self and make your cash work more durable.
Transfer to a Excessive-Yield Financial savings Account. After the Dec. 14 hike, probably the most beneficiant financial savings accounts will yield 3.50% or higher. That’s a lot decrease than the inflation charge, but it surely’s higher than conventional large banks’ paltry financial savings yields, which haven’t budged throughout this mountain climbing cycle. Transfer your cash in the event you haven’t already.Pay Off Your Credit score Card Balances. You need to by no means carry a bank card steadiness in the event you can keep away from it, but it surely’s particularly painful when rates of interest are excessive. Make a plan to repay your present balances as quickly as you’ll be able to. Should you need assistance, work with a nonprofit credit score counseling company.Purchase Sequence I Bonds Earlier than Could 2023. They’re your greatest guess to battle inflation, higher than any financial savings account. Charges reset twice per 12 months, on Nov. 1 and Could 1. With inflation most likely at its peak, the Could 1 charge is more likely to be decrease than the present 6.89% charge, which is already down from 9.62% earlier this 12 months. Purchase a New Automobile Sooner Than Later. Auto loans are a bizarre vivid spot for customers to this point this mountain climbing cycle. Supplier financing charges haven’t elevated a lot since 2021 as automobile sellers battle softening demand for brand new vehicles whereas undercutting banks and credit score unions that additionally supply auto loans. Plus, each new and used automobile costs are coming right down to earth as provide will increase and demand cools.
How We Obtained Right here: Fed Funds Fee Hikes in 2022
The FOMC has raised charges at a breakneck tempo in 2022.
The present goal charge of three.75% to 4% is 375 foundation factors larger than it was initially of the 12 months. The hole is more likely to enhance to 425 foundation factors after the December assembly.
Markets and economists count on a 25-point charge hike on the FOMC’s subsequent assembly, which concludes on Feb. 1, 2023, and one other 25-point hike on the FOMC’s March 2023 assembly. After that, expectations are a lot much less clear. Some imagine the Fed will pause hikes indefinitely, whereas others count on cumulative will increase of as a lot as 100 foundation factors extra in 2023.
All of it comes again to what the financial system does within the meantime. Hotter-than-expected inflation readings or job progress numbers in Q1 2023 may persuade the Fed to hike longer and better than anticipated, even when it ends in an extended, deeper recession than forecast. If the financial system seems to be cooling sooner than anticipated, it’s not out of the query that the Fed does nothing on Feb. 1.
In that case, markets will inevitably stay up for the following large query of the present Fed cycle: when and by how a lot it’ll begin reducing the federal funds charge.
The speedy enhance comes after two years of rock-bottom rates of interest. The Fed slashed charges by 150 foundation factors between February and April 2020 because the COVID-19 pandemic pummeled the financial system. They stayed close to zero by 2021.
One Extra Fed Transfer to Watch: Quantitative Tightening
The FOMC’s rate of interest choices would possibly seize headlines, however they’re not the one strikes the Fed makes to steer the financial system.
Because the Nice Monetary Disaster of the late 2000s, the Fed has been within the enterprise of shopping for, holding, and (often) promoting U.S. authorities bonds and different authorities securities. When the Fed buys securities, it’s known as quantitative easing (QE). When it sells them or permits them to mature with out changing them, it’s known as quantitative tightening (QT).
Quantitative easing will increase the U.S. greenback provide, which is why some say the Fed “prints cash” in response to financial weak spot. Quantitative tightening decreases the greenback provide, although you don’t hear a lot in regards to the Fed “burning cash” to battle inflation.
Quantitative Tightening in 2022
The Fed purchased greater than $4 trillion in authorities securities between early 2020 and early 2022, including to a large stockpile left over from the Nice Monetary Disaster. It started QT in June 2022 and accelerated the tempo in September.
Since then, the Fed has decreased its steadiness sheet by about $95 billion every month. However with practically $9 trillion nonetheless on its books, it’ll take greater than 7 years to totally unwind its purchases. That’s far longer than economists count on the present cycle of rate of interest hikes to final — and assumes no financial crises that demand quantitative easing between every now and then.
Why Quantitative Tightening Issues for You
QT isn’t some summary high-finance maneuver. By rising the availability of U.S. authorities bonds, it places upward strain on charges, compounding the consequences of fed funds charge hikes. For instance, the yield on the carefully watched 10-year U.S. Treasury invoice jumped from about 1% in January 2021 to about 4% in late October 2022.
The mixed impact of QT and fed funds charge hikes exhibits up in rates of interest tied to each benchmarks, like mortgage charges. That’s why the common 30-year fastened charge mortgage charge elevated by about 450 foundation factors between January 2021 and October 2022 — in contrast with simply 300 foundation factors for the federal funds charge.
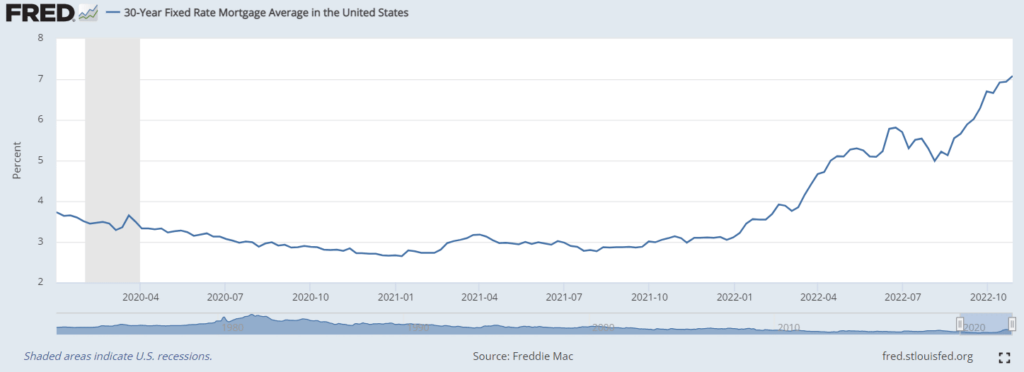
So in the event you’re available in the market for a brand new home or need to open a house fairness line of credit score quickly, the fed funds charge received’t inform the entire story. If the Fed accelerates QT, bond yields — and thus mortgage charges — may proceed to rise even after charge hikes stop and inflation floats right down to historic norms.























