World shares and bonds misplaced greater than $30tn for 2022 after inflation, rate of interest rises and the struggle in Ukraine triggered the heaviest losses in asset markets for the reason that international monetary disaster.
The broad MSCI All-World index of developed and rising market equities has shed a fifth of its worth this yr, the largest decline since 2008, with shares from Wall Avenue to Shanghai and Frankfurt all notching up vital falls.
In New York, a sell-off on the final buying and selling day of the yr added to losses for the blue-chip S&P 500 and the tech-heavy Nasdaq, which have fallen 19 per cent and 33 per cent this yr, respectively, the worst annual efficiency for each since 2008.
Bond markets have additionally endured heavy promoting: the US 10-year authorities bond yield, a worldwide benchmark for long-term borrowing prices, has shot as much as 3.9 per cent from about 1.5 per cent on the finish of final yr — the largest annual improve in Bloomberg data stretching to the Nineteen Sixties.
“We had this example for years the place equities and bonds had been each costly as a result of they had been the identical sport, pushed by low inflation and low rates of interest,” stated Luca Paolini, chief strategist at Pictet Asset Administration. “The lesson of this yr is that in some unspecified time in the future there’s a day of reckoning, and when it comes it’s brutal.”
The market worth of corporations traded throughout all international inventory exchanges tumbled by $25tn, in response to Bloomberg, whereas the information supplier’s Multiverse index, which tracks international authorities and company debt, is down nearly 16 per cent or $9.6tn in market worth phrases, in response to provisional calculations at Thursday’s market shut.
Antonio Cavarero, head of investments at Generali Insurance coverage Asset Administration, described shares’ and bonds’ joint downward trajectories as “a game-changer for traders”. This contrasts with 2008, when the droop was targeting equities whereas bond costs rose and dealt a painful blow to many traders who construct portfolios within the hope that fixed-income holdings will act as a ballast when equities markets tumble.
The losses got here after central banks led by the US Federal Reserve ratcheted up borrowing prices in an try to manage the worst spell of inflation in a long time.
These rate of interest rises delivered to a dramatic shut the period of low-cost cash that adopted the monetary disaster, which squeezed down the yields on protected authorities debt under zero and pushed up the costs of even the riskiest belongings, notably within the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February additionally infected a extreme bout of inflation, disrupting provide chains. An 8 per cent surge within the US greenback in opposition to a basket of half a dozen main friends has positioned additional stress on many markets.
Surging borrowing prices additionally wiped trillions of {dollars} off the worth of the US’s tech titans, which had led the pandemic-era rally starting in 2020.
Tesla, the electrical carmaker, has shed nearly two-thirds of its worth this yr, whereas chipmaker Nvidia has dropped 50 per cent. US tech heavyweights Apple and Microsoft have tumbled nearly 30 per cent, whereas Google guardian Alphabet is off practically 40 per cent and Fb proprietor Meta has plummeted 64 per cent.
The worth of the cryptocurrency market has tumbled by $1.7tn for the reason that begin of 2022, in response to Monetary Instances knowledge, in an indication of how the speculative fervour that took maintain in 2020 has burst this yr.
China’s sprawling equities markets additionally sustained a blow because the financial system was disrupted by strict zero-Covid measures and the nation is now battling an enormous wave of infections because it opens up once more. The CSI 300 measure of shares in Shanghai and Shenzhen fell 22 per cent in native foreign money phrases and 28 per cent in greenback phrases.
The MSCI Europe index is down about 16 per cent in greenback phrases, however a slimmer 11 per cent in euros.
Commodities have been among the many uncommon gainers in international markets this yr: the broad S&P GSCI gauge has rallied 9 per cent, with vitality and agriculture costs posting robust positive factors.
London’s FTSE 100, which is closely weighted in direction of vitality, mining and pharmaceutical corporations, which have fared higher on this yr’s market shift, is up barely for the yr thus far in sterling phrases.
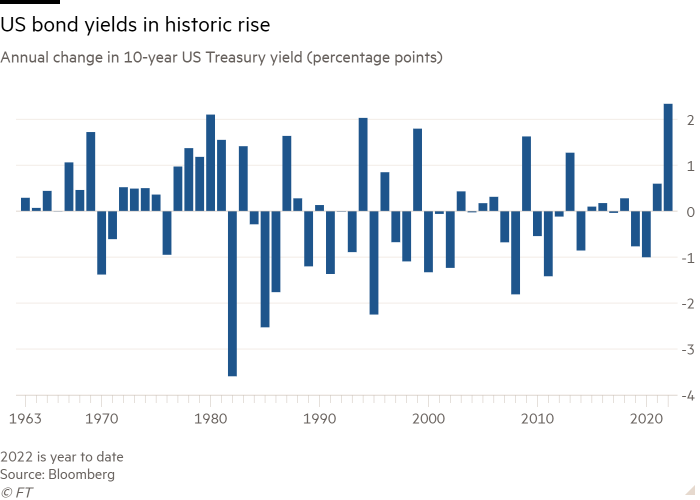
The depth of this yr’s market swings highlights the size of regime change confronted by international traders, who had grown accustomed to low rates of interest.
Greater rates of interest dent the attraction of holding belongings similar to shares and riskier debt as a result of traders are in a position to earn higher returns in money or ultra-safe belongings similar to US, German or Japanese authorities bonds. Since larger charges make borrowing dearer, additionally they have a tendency to put stress on the broader financial system by tightening monetary situations for corporations and companies.