rarrarorro/iStock by way of Getty Photographs
The Malaysian financial system grew at a tempo of 5.6% year-on-year (y/y) within the first quarter of 2023, exhibiting continued fast growth after annual financial development of 8.7% in 2022. The buoyant tempo of financial development in 2022 was the quickest annual GDP development price since 2000.
The tempo of growth of the Malaysian financial system is predicted to reasonable throughout 2023 on account of numerous headwinds, together with the influence of excessive base yr results and slowing merchandise export development. Nonetheless, an necessary constructive issue is predicted to be the continued gradual restoration of worldwide tourism visits from Asia, the Center East, and Europe.
Malaysian financial system maintains constructive momentum in Q1 2023
The Malaysian financial system grew at a tempo of 5.6% y/y within the first quarter of 2023, after rising at 7.1% y/y within the fourth quarter of 2022. Measured on a quarter-on-quarter (q/q) foundation, the Malaysian financial system grew by 0.9% q/q within the first quarter of 2023, marking a pointy turnaround after a contraction of 1.7% q/q within the fourth quarter of 2022.
S&P International Market Intelligence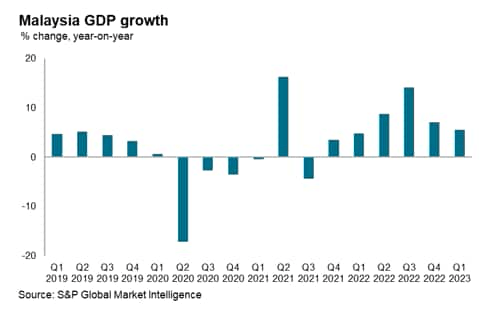
Helped by robust home demand, the Malaysian providers sector continued to indicate fast development of seven.3% y/y within the first quarter of 2023, following development of 9.1% y/y within the fourth quarter of 2022. The tempo of growth within the development sector additionally remained robust, rising by 7.4% y/y within the first quarter of 2023, after fast development of 10.1% y/y within the fourth quarter of 2022. Nonetheless, development within the manufacturing sector has moderated in current quarters, rising by 3.2% y/y within the first quarter of 2023, just like the three.9% y/y tempo within the fourth quarter of 2022.
The seasonally adjusted S&P International Malaysia Manufacturing Buying Managers’ Index (PMI) was unchanged at 48.8 in April, signalling that enterprise situations remained difficult for corporations. That stated, the index was at its joint-highest degree since September 2022, suggesting a tentative restoration in working situations in current months.
S&P International, Division of Statistics Malaysia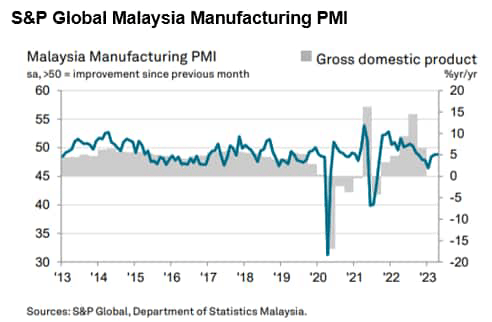
Throughout 2022, an necessary constructive issue for the Malaysian manufacturing sector was the power of producing exports. General, Malaysian merchandise exports have carried out strongly throughout 2022, with exports rising by 25% y/y. Exports of manufactured items rose by 22% y/y throughout 2022, boosted by exports {of electrical} and digital merchandise, which rose by 30%.
Rising world commodity costs additionally boosted commodities exports, with mining exports up by 68% y/y on account of robust exports of oil and fuel, whereas agricultural exports rose by 23%.
In 2023, the tempo of export development is predicted to reasonable, reflecting base yr results in addition to the financial slowdown in key markets, notably the US and EU. Items exports within the first quarter of 2023 rose by 2.8% y/y, with the tempo of export development moderating considerably in contrast with 2022.
As mainland China is Malaysia’s largest export market, accounting for 15.5% of whole exports, the persevering with rebound in mainland China’s financial system throughout 2023 might assist to mitigate the influence of softening merchandise exports to the US and EU.
Nonetheless worldwide tourism is predicted to strengthen throughout 2023, as vacationer arrivals from main tourism markets in ASEAN, the Center East, and Europe proceed to get well, whereas Chinese language vacationer arrivals steadily enhance. Tourism Malaysia is concentrating on 16.1 million worldwide customer arrivals for 2023, a 60% improve in contrast with the estimated 10.1 million worldwide customer arrivals in 2022. This compares with the pre-pandemic degree of 26.1 million worldwide customer arrivals in 2019. In 2019, whole home and worldwide tourism was estimated to have accounted for round 16% of gross worth added to Malaysia’s whole GDP.
MATRADE; EC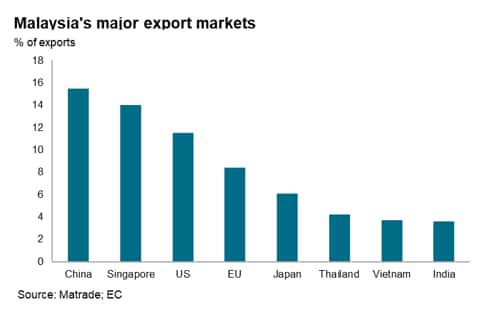
Inflation pressures have been steadily easing
Diminished demand for inputs helped result in an enchancment in vendor efficiency, with improved capability at suppliers and an absence of port congestion additionally aiding a discount in lead occasions. Suppliers’ supply occasions shortened for the fourth successive month and to one of many best extents up to now decade. There have been additional indicators of uncooked materials costs levelling off in April as enter prices rose solely barely. The speed of inflation was broadly consistent with the 34-month low posted in March.
S&P International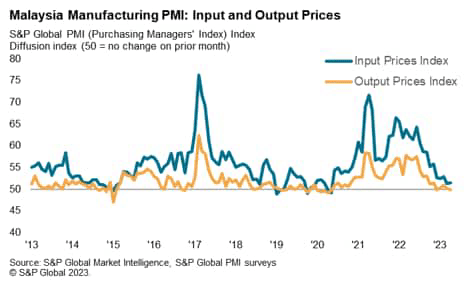
In Malaysia, CPI inflation pressures have begun to steadily reasonable, easing to a tempo of three.4% in March 2023, in contrast with 4.5% y/y in September 2022.
In 2022, Malaysia’s central financial institution, Financial institution Negara Malaysia (BNM), diminished the diploma of financial lodging in a collection of tightening steps. The latest financial coverage tightening was on third Might 2023, when the Financial Coverage Committee determined to extend the In a single day Coverage Charge (OPR) by 25 foundation factors (bps) to three.0 p.c.
The MPC expects that each headline and core inflation will reasonable over the course of 2023, averaging between 2.8% and three.8%. Nonetheless, core inflation will stay at elevated ranges amid agency demand situations. Current value controls and gasoline subsidies will proceed to partially comprise the extent of upward pressures on inflation.
Moderating international electronics demand provides to headwinds
{The electrical} and electronics (E&E) sector has been an necessary driver of Malaysia’s manufacturing exports. Exports of E&E merchandise, which accounted for 38% of merchandise exports, rose by 30% y/y in 2022. This fast development was pushed by strong international demand for semiconductors, reflecting technological tendencies corresponding to 5G rollout, cloud computing, and the Web of Issues. Exports of built-in circuits grew by 33% y/y in 2022, whereas exports of components for built-in circuits rose by 120% y/y. The mixed exports of built-in circuits and components accounted for 58% of Malaysia’s whole exports of E&E merchandise in 2022.
The worldwide electronics manufacturing trade slowed within the second half of 2022 because of the weakening tempo of financial development within the US, EU, and China.
Malaysian exports {of electrical} and digital merchandise fell by 4.4% year-on-year in March 2023.
Latest S&P International survey knowledge signifies that the worldwide electronics manufacturing trade is going through headwinds from the weakening tempo of worldwide financial development. The headline seasonally adjusted S&P International Electronics PMI fell from 51.4 in February to 48.4 in March, weakening additional in April to 48.2. This signalled renewed deterioration in working situations throughout the worldwide electronics manufacturing sector as key client markets for electronics, notably the US and EU, remained weak.
Malaysian exports {of electrical} and digital merchandise fell by 4.4% year-on-year in March 2023. Malaysia’s E&E trade is predicted to face persevering with comfortable financial situations throughout 2023, in contrast with the very fast tempo of growth in 2022. The newest knowledge indicated a renewed contraction within the international electronics sector, reflecting additional declines in new orders and output.
S&P International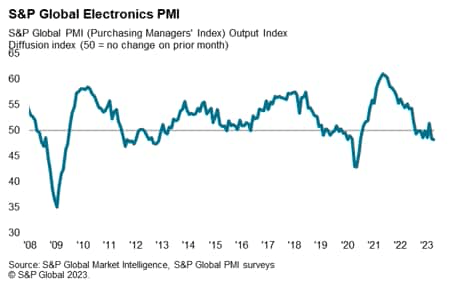
Demand situations for the worldwide electronics trade have remained weak since early 2023. Subdued shopper demand weighed on new enterprise positioned with electronics producers, as new orders fell for the ninth time up to now ten months. Inflationary pressures and international financial uncertainty had been typically cited by panellists as elements dampening demand.
New orders within the Client Electronics phase fell on the quickest tempo for six months, whereas there was a renewed decline in Industrials, the primary since January. Computing noticed a slower contraction whereas demand situations for the Communications phase stabilized.
S&P International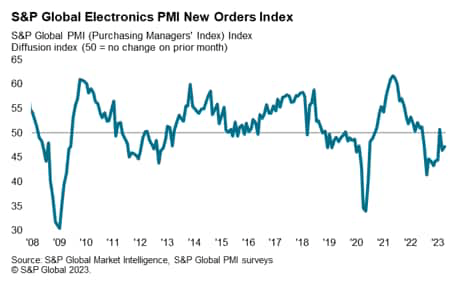
Financial outlook
The Malaysian financial system rebounded strongly throughout 2022, with financial development momentum boosted by the easing of COVID-19 restrictive measures in addition to buoyant exports {of electrical} and digital merchandise, palm oil merchandise in addition to oil and fuel exports.
In 2022, larger world oil and fuel costs on account of the Russia-Ukraine battle boosted Malaysian vitality exports and contributed to larger fiscal revenues. Malaysia additionally benefited from larger common palm oil costs, on account of disruptions to world edible oil markets, together with Ukrainian exports of sunflower oil.
Throughout 2023, development momentum is predicted to reasonable on account of base yr results and the slowdown of merchandise exports. Nonetheless, the reopening of worldwide borders throughout the Asia-Pacific area, notably in mainland China, will assist the continued gradual restoration of the worldwide tourism trade, which was an necessary a part of the Malaysian financial system previous to the pandemic. This can assist to mitigate the influence of slower development for merchandise exports. Home demand is predicted to be resilient in 2023, helped by the development in labour market situations. Easing restrictions on the entry of migrant labor will even steadily assist to assist trade sectors which can be reliant on overseas employees.
There are a selection of draw back dangers to the near-term development outlook, notably because of the slowdown in world development. Malaysia’s export sector is susceptible to protracted weak financial development momentum within the US and EU, which collectively account for round one-fifth of whole exports. Nonetheless, the easing of COVID-19 restrictions in mainland China might assist to spice up Malaysian exports to this key market, which is Malaysia’s largest export market and accounts for round 15% of whole exports.
Regardless of the slowdown in international electronics orders in current months, the medium-term financial prospects for Malaysia’s electronics trade are beneficial. The outlook for electronics demand is underpinned by main technological developments, together with the 5G rollout over the following 5 years, which is able to drive demand for 5G cellphones.
Demand for industrial electronics can be anticipated to develop quickly over the medium time period, helped by Business 4.0, as industrial automation and the Web of Issues increase fast development in demand for industrial electronics.
Malaysia’s competitiveness as a worldwide electronics hub has been highlighted by the choice of numerous electronics multinationals to put money into large-scale new initiatives. Intel (INTC) is investing USD 7 billion in a brand new semiconductors packaging plant in Penang, which is estimated to be accomplished by 2024 and create hundreds of latest jobs in Malaysia. Infineon Applied sciences (OTCQX:IFNNY) is developing a brand new state-of-the-art wafer fab module in Kulim, with round Ringgit 8 billion in funding. The brand new module, which is predicted to be accomplished in 2024, will add important manufacturing capability to energy semiconductors.
S&P International Market Intelligence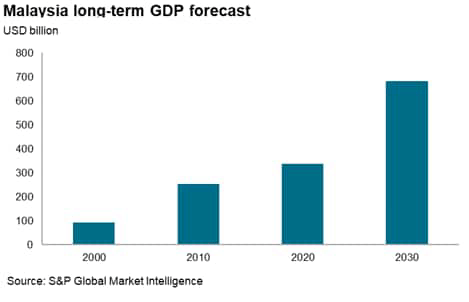
General, the medium- to long-term development outlook for Malaysia stays beneficial, with whole nominal GDP measured in USD phrases forecast to rise from round USD 400 billion in 2022 to USD 680 billion by 2030 and USD 780 billion by 2032. In the meantime, per capita GDP is projected to rise from USD 12,000 in 2022 to USD 18,600 by 2030, which is able to assist to drive the expansion of the home client market.
Unique Publish
Editor’s Be aware: The abstract bullets for this text had been chosen by Looking for Alpha editors.























