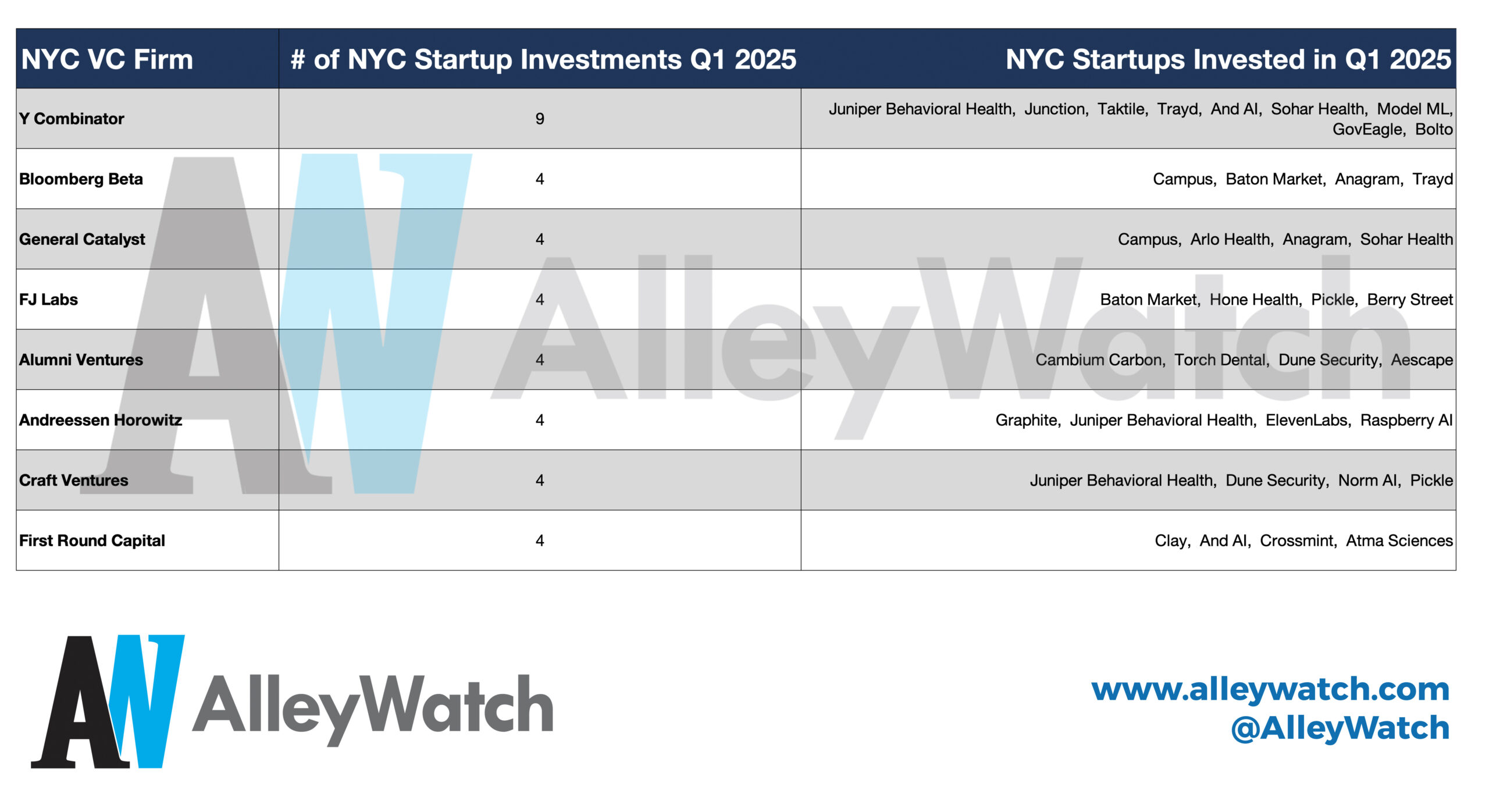
Markets predict 100% likelihood of Financial institution of England charge hike in June
The inflation knowledge has meant {that a} additional rate of interest hike on the Financial institution of England’s subsequent financial coverage assembly is assured, in keeping with monetary markets at the least.
Economics correspondent Richard Partington reviews:
Markets are totally pricing in one other Financial institution charge improve of 1 / 4 level in June, with an outdoor likelihood of a good larger half level rise. Markets anticipate the bottom charge may attain a peak of virtually 5.4% earlier than the tip of the yr, virtually a complete proportion level greater than the present degree.
You may see what traders are pondering within the under desk. The Financial institution of England’s financial institution charge rose to 4.5% earlier this month. Derivatives trades present that markets are totally pricing in an extra improve on 22 June, with financial institution charge anticipated to rise to above 5.35% by December earlier than dropping again.
Key occasions
Germany companies are getting extra pessimistic, in keeping with an indicator carefully watched by economists.
The Ifo Institute’s longstanding survey index slid to 91.7 factors in Might, from a revised 93.4 in April, effectively under the consensus expectation of 93.
UK bond traders are scrambling to readjust to this morning’s shock inflation knowledge. Only a few economists have been anticipating it to come back in fairly so excessive.
UK bond yields (which transfer inversely to costs) have risen sharply as traders offered. The yield on 10-year UK authorities bonds (often called gilts) rose above 4.3% on Wednesday, up from 4.2% on Tuesday.
That was the very best degree for the 10-year since October 2022, when a sure Liz Truss was in energy. The disastrous “mini-budget” delivered by her former chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng prompted 10-year yields to surge above 4.6%.
The yield dropped again to under 3% after Rishi Sunak and Jeremy Hunt have been put in by a stricken Tory celebration. However yields have crept up over the past three months as inflation has hung round. The ten-year yield began the week under 4%.
Increased rates of interest are likely to imply the steady earnings from bonds are much less precious, so bond costs fall and yields rise.
In the meantime the pound has given up all of its earlier good points. It’s now down by 0.04% towards the US greenback for the day at $1.2405.
Normally greater rates of interest additionally make the native forex extra engaging. However that solely works up to a degree. If charges rise too excessive then merchants can begin to worry that it’s going to choke off financial development.
Bloomberg Information has some useful evaluation:
The pound has undone all of its advance following the inflation knowledge after which some. That’s doubtless as a result of merchants weighing the prospect of extra Financial institution of England charge hikes – sometimes constructive for the forex – towards the financial slowdown that would comply with quickly after.

Sarah Butler

Sticking with company information for a second, the share value of Marks & Spencer has surged by 12% within the first two hours of buying and selling after it smashed forecasts.
Marks & Spencer income have elevated by greater than a fifth, beating Metropolis expectations, with the retailer crediting the rise to enhancements to the model credentials of its clothes and extra inexpensive meals.
Nevertheless, the corporate warned that it confronted a difficult yr forward as prices continued to extend. It expects to spend £100m extra on employees wages and £50m on vitality.
It stated these rises could be offset by measures reminiscent of extra automated tills and the closure of about 20 shops, as already introduced, about half of which might be relocated, together with new flagship shops in Liverpool, Leeds, Manchester, Birmingham and Thurrock.
You may learn the total report right here:
Power agency SSE reviews close to doubling of annual income
Jillian Ambrose

SSE has reported a close to doubling of its annual income in contrast with the yr earlier than after hovering vitality market costs led to a increase for its fossil gas energy vegetation.
The Perth-based firm stated its adjusted pre-tax income climbed to £2.18bn for the 12 months to the tip of March, up from virtually £1.16bn the yr earlier than.
The sharp improve in full-year income got here as earnings from its gas-fired energy vegetation surged virtually four-fold to £1.24bn for the final monetary yr, up from £331.1m the yr earlier than.
The corporate has sought to downplay the hovering income generated by its gasoline vegetation within the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which triggered the leap in international vitality market costs that has ignited requires a windfall tax on the surplus income made by energy turbines and oil firms.
Shares within the firm rose by 1.4% on Wednesday morning.
You may learn the total report right here:

A former member of the Financial institution of England’s financial coverage committee has stated he fears that inflation is turning into “embedded” within the UK financial system – significantly in indicators that wages are persevering with to rise.
Sushil Wadhwani, who’s now chief funding officer at PGIM Wadhwani, stated the most recent inflation knowledge was “extremely disappointing”, highlighting excessive inflation in providers costs. (Wadhwani is a former member of the Scott Belief, the physique that controls the Guardian.)
Wadhwani informed the BBC’s In the present day programme:
The important thing factor is about these numbers in the present day just isn’t solely that they have been disappointing in the present day, however they’ve been disappointing for a number of months. What’s starting to fret me – and maybe extra importantly to fret the Financial institution – is that inflation is turning into embedded, that individuals are anticipating inflation to remain excessive for longer. That clearly a harmful improvement.
It could seem that wage development is staying stubbornly excessive – understandably, I ought to say, given how excessive headline inflation is. However wage inflation is remaining excessive.
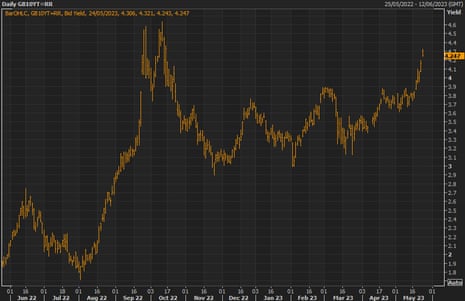
Markets predict 100% likelihood of Financial institution of England charge hike in June
The inflation knowledge has meant {that a} additional rate of interest hike on the Financial institution of England’s subsequent financial coverage assembly is assured, in keeping with monetary markets at the least.
Economics correspondent Richard Partington reviews:
Markets are totally pricing in one other Financial institution charge improve of 1 / 4 level in June, with an outdoor likelihood of a good larger half level rise. Markets anticipate the bottom charge may attain a peak of virtually 5.4% earlier than the tip of the yr, virtually a complete proportion level greater than the present degree.
You may see what traders are pondering within the under desk. The Financial institution of England’s financial institution charge rose to 4.5% earlier this month. Derivatives trades present that markets are totally pricing in an extra improve on 22 June, with financial institution charge anticipated to rise to above 5.35% by December earlier than dropping again.
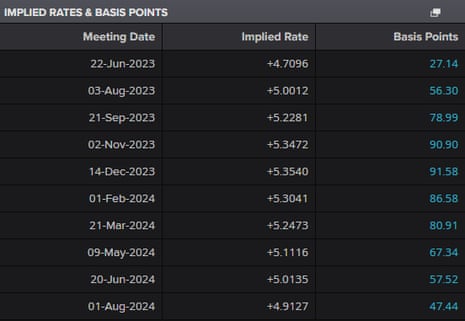
The monetary market response on Wednesday morning has been centered not on inflation falling, however on it falling lower than anticipated – client value index inflation hit 8.7% in comparison with common forecasts of 8.2% from economists.
That has prompted a flurry of shopping for sterling on forex markets as merchants reposition. The guess is that greater inflation persuades the Financial institution of England to boost rates of interest additional. That makes sterling extra engaging as a result of traders could make greater returns.
You may see the consequences on this chart displaying the pound’s efficiency towards the greenback in a single day. It jumped as excessive as $1.2465 after the info was launched, earlier than dropping again.
On the time of writing sterling was up by 0.15% towards the US greenback.
It’s a promoting day on the FTSE 100 – doubtless as merchants alter to the expectation of upper rates of interest. The index has dropped by 1.6%.
Solely two firms have elevated share costs up to now in the present day: product testing firm Intertek after it reported greater gross sales, and vitality agency SSE, which reported massive income.
The largest fallers are property firms: Taylor Wimpey, Persimmon, Barratt Developments and British Land are all down by between 3.6% and 4.6%.
Inflation drops however costs of sugar, olive oil and eggs drive steep meals value rises
UK inflation dropped to eight.7% within the yr to April, the primary time it has dropped under 10% since August and the bottom since March 2022.
But that steep fall – lengthy anticipated due to the large improve in vitality costs in April 2022 – has not all been pleased information. It was much less dramatic than anticipated by economists.
Right here is the total report by the Guardian’s Richard Partington:
And core inflation, which makes an attempt to measure the underlying value pressures, truly rose between March and April.
In the meantime, the politically delicate will increase in meals costs have been sustained. Meals costs rose by almost a fifth throughout the yr to April. Listed below are a number of the parts of that 19% meals value inflation:
Sugar 47.4%
Olive oil 46.4%
Eggs 37%
Low-fat milk 33.5%
Cheese and curd 30.6%
Flours and different cereals 30%
Pasta merchandise and couscous 27.7%
Prepared-made meals 20.8%
Butter 20.1%
Bread 18.6%
Jams, marmalades and honey 17.9%
Fish 14.2%
Pizza and quiche 11.9%
Fruit 10.8%
James Smith, a developed markets economist at ING, an funding financial institution, says:
UK inflation has are available in greater than just about anybody, together with members of the Financial institution of England’s committee, anticipated in April.
This undoubtedly makes life more durable for policymakers and little doubt raises the prospect of yet one more 25bp charge hike in June.
As an alternative, it’s meals costs that are actually the largest headache. […] Assuming the newest month-on-month will increase in output costs have been to proceed by way of the rest of this yr, it implies that meals inflation ought to be again to the 6% space or under by Christmas.
Rachel Reeves, Labour’s shadow chancellor, is specializing in meals costs (as did her Conservative counterpart).
The truth of in the present day’s inflation figures are hovering meals costs staying excessive and hitting households onerous.
After 13 years of Tory authorities, by no means have folks paid a lot however obtained so little in return. Labour will shield household funds and construct our financial safety.
— Rachel Reeves (@RachelReevesMP) Might 24, 2023
However it’s the core inflation quantity that’s catching the attention of many analysts.
Inflation falls from 10.1% to eight.7% however…- dangerous information for Financial institution of England = core inflation rose from 6.2% to six.8%. – dangerous information for households = meals value inflation is stubbornly excessive at 19.1% and shifting centre stage in the price of residing disaster
— Torsten Bell (@TorstenBell) Might 24, 2023
So-so UK #inflation knowledge.
Excellent news is that the headline CPI charge fell sharply, from 10.1% to eight.7%, however this was completely accounted for by the autumn in #vitality value inflation.
Every thing else trying sticky 👇
Core charge excl. meals & vitality hit a brand new excessive of 6.8%, up from 6.2%. pic.twitter.com/6bJgBdSqK8
— Julian Jessop (@julianHjessop) Might 24, 2023
Inflation is the important thing theme for this morning’s First Version e-newsletter – and its editor, Archie Bland, has been speaking to the Guardian’s economics correspondent, Richard Partington, about why the speed has dropped.
It contains this useful rationalization of what economists name “base results” – or why the very fact of costs staying the identical to a yr in the past results in a drop within the headline inflation charge.
“Initially of April 2022, there was a roughly 50% rise in gasoline and electrical energy payments when Ofgem elevated the value cap,” Richard stated. “That was an eyewatering determine. Now the comparability interval is with the already excessive degree after that rise occurred, so the speed drops.” Positive sufficient, the ONS stated that electrical energy and gasoline costs contributed 1.42 proportion factors to the autumn.
And on the Financial institution of England’s dilemma:
“The monetary markets predict the Financial institution to boost rates of interest yet one more time,” Richard stated. “They’re at present 4.5% – the very best charge since 2008 – and the expectation is that they go to 4.75% after which keep there for a while.” This morning’s figures don’t change that expectation: rates of interest take a while to filter by way of into the inflation charge, so it could take a very radical deviation from what was anticipated to immediate a unique course to the one already being plotted out.
You may signal as much as the e-newsletter by clicking right here.
The headline inflation charge could also be falling, however there are additionally different indicators that the UK just isn’t finished with value pressures simply but: core inflation is at its highest since 1992.
Core inflation is a measure carefully watched by economists as a result of it strips out probably the most unstable parts of the index – like meals, vitality, alcohol and tobacco – in an effort to work out the underlying image.
For the Financial institution of England, that provides to stress to maintain on elevating rates of interest to chill inflation.
Paul Dales, chief UK economist at Capital Economics, a consultancy, stated:
The smaller-than-expected fall in CPI inflation from 10.1% in March to eight.7% in April (BoE 8.4%, consensus 8.2%, CE 8.0%) means it’s now very onerous to think about the Financial institution of England not elevating rates of interest from 4.50% to 4.75% in June.
“The majority of the autumn was as a result of a plunge in utility value inflation,” he famous.
However way more necessary was the worrying giant rebound in core inflation from 6.2% in March to six.8% in April (consensus 6.2%, CE 6.1%). That took it above what all of us thought was the height of 6.5% in September of final yr and to the very best charge since 1992.
Jeremy Hunt has stated that meals value inflation remains to be rising too rapidly – an acknowledgement of its political significance.
Halving inflation is certainly one of 5 key targets for the federal government (albeit one they’re virtually sure to hit as the consequences of earlier vitality value will increase cross by way of the info).
Hunt, the chancellor, stated:
The IMF stated yesterday we’ve acted decisively to deal with inflation however though it’s constructive that it’s now in single digits, meals costs are nonetheless rising too quick. So in addition to serving to households with round £3,000 of value of residing help this yr and final, we should stick resolutely to the plan to get inflation down.
This chart from the Workplace for Nationwide Statistics exhibits simply how steep meals value inflation has been within the final yr.
Meals value inflation is especially necessary as a result of it’s keenly felt by poorer households, who spend a larger proportion of their earnings on necessities.
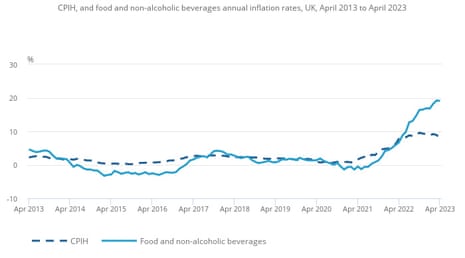
(Please observe that this chart exhibits the marginally completely different client value index together with proprietor occupiers’ housing prices, or CPIH, which the ONS insists upon utilizing. For now, the Financial institution of England and others nonetheless take a look at the straight client value index, or CPI, from which we’re additionally quoting.)
Meals value inflation stays close to 45-year excessive
Whereas the general drop in inflation might be welcomed, there’s restricted consolation when meals costs: costs for meals and non-alcoholic drinks rose by 19% within the yr to April.
That was solely a marginal drop from the 19.1% charge in March.
The Workplace for Nationwide Statistics’ indicative modelled estimates counsel that the annual charge for foods and drinks in April 2023 is the second highest seen for over 45 years, when the speed in August 1977 was estimated to be 21.9%.
As anticipated, it’s vitality costs that brought on the large drop in annual inflation within the yr to April.
The UK’s Workplace for Nationwide Statistics stated:
Electrical energy and gasoline costs contributed 1.42 proportion factors to the autumn in annual inflation in April as final April’s rise dropped out of the annual comparability, however this element nonetheless contributed 1.01 proportion factors to annual inflation.
This time final yr, international vitality costs had surged after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. These value rises are actually baked in to the figures, so the headline inflation determine is falling.
UK inflation drops to eight.7%
Newsflash: UK client value index inflation has dropped to eight.7%, the bottom since March 2022.
Nevertheless, that was nonetheless greater than the typical expectation of 8.2% in a ballot of economists. Extra element to come back.
UK inflation forecast to drop under 10%
Good morning, and welcome to our stay, rolling protection of enterprise, economics and monetary markets.
The surge in inflation over the past two years has turn out to be a key precedence for the UK authorities. However since peaking at an annual charge of 11.1% in October – a 41-year excessive – inflation has been dropping again quickly. Knowledge to be printed shortly will present whether or not value rises have slowed additional.
Economists count on the annual charge of client value index inflation to fall from 10.1% in March to eight.2% in April, in keeping with a ballot by Reuters.
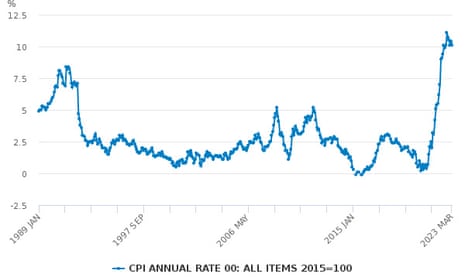
The spike in inflation has two primary causes: first, the disruption from the coronavirus pandemic that fouled up provide chains around the globe and added prices; and second, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which prompted chaos on international vitality markets as nations around the globe scrambled to seek out alternate options to Russian oil and gasoline. For probably the most half, they have been profitable, however costs however rose.
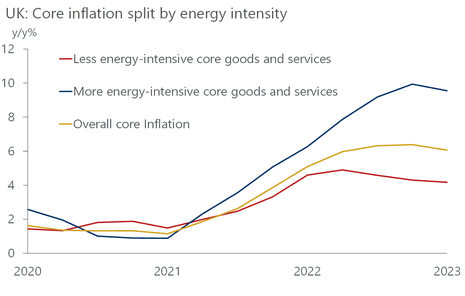
The vitality disaster has been a big contributor to more moderen value will increase. Because the under chart from consultancy Oxford Economics exhibits, the merchandise that take probably the most vitality to make have been most affected by inflation.
Financial institution of England governor Andrew Bailey is making not one however two public appearances in the present day. The Financial institution’s financial policymakers must resolve whether or not falling inflation means they need to ease off additional rates of interest will increase, or whether or not they’re nonetheless uncomfortable with a charge that may virtually actually be effectively above their 2% goal.
Bailey on Tuesday stated he believed that inflation has “turned the nook”, which could counsel that additional vital tightening of financial coverage by way of greater charges won’t be essential. Alternatively, a brighter financial outlook for the UK – recognised by the Worldwide Financial Fund on Tuesday – may give weight to the “hawks” on the financial coverage committee who need greater charges to maintain on taming inflationary pressures.
The agenda
7am BST: UK inflation knowledge (April; earlier: 10.1% year-on-year; consensus: 8.2%)
9am BST: Germany Ifo enterprise local weather index (Might; prev.: 93.6 factors; cons.: 93)
10:30am BST: Andrew Bailey: speech at Mansion Home internet zero supply summit
11am BST: UK Confederation of British Trade industrial traits (Might; prev.: -20 factors; cons.: -19)
2pm BST: Andrew Bailey: interview on “inflation and the financial system”